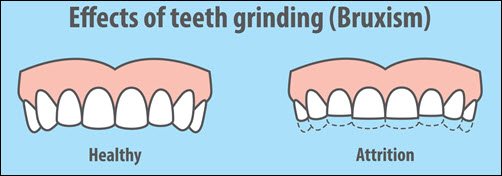
Tooth Grinding: Bruxism and Tooth Attrition
Bruxism, commonly known as teeth grinding, is a condition that can lead to significant dental health issues, including tooth attrition. This involuntary grinding or clenching of the teeth, especially during sleep, often goes unnoticed until complications arise. Understanding bruxism and its impact on your teeth is crucial for maintaining good oral health.
What is Bruxism?
Bruxism is often categorized into two types: “awake”, where teeth grinding happens during waking hours, often due to stress, anxiety, or concentration; and “sleep”, a sleep-related movement disorder. People with sleep bruxism are more likely to have other sleep disorders, such as snoring or sleep apnea.
Symptoms of Bruxism:
- Grinding noises during sleep
- Flattened, fractured, chipped, or loose teeth
- Worn tooth enamel, exposing deeper layers of the tooth
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Jaw or face pain and soreness
- Tired or tight jaw muscles
- Dull headache originating in the temples
- Damage from chewing on the inside of the cheek
- Sleep disruption
Consequences: Tooth Attrition and Beyond
Tooth attrition, the wearing down of the tooth’s surface due to grinding, is a primary concern with bruxism. This can lead to dental sensitivity and can also alter the appearance of your teeth, making them shorter and affecting your smile. In severe cases, grinding can lead to jaw disorders, headaches, and damaged teeth requiring crowns or dental restorations.
Managing Bruxism and Preventing Tooth Attrition
- Custom-Fitted Night Guards: The most common treatment for sleep bruxism is wearing a night guard. These custom-made devices fit over the top or bottom teeth and protect them from grinding.
- Stress Reduction: Since stress is a significant factor in bruxism, relaxation techniques such as meditation, counseling, and exercise can be beneficial.
- Dental Correction: Misaligned teeth or an abnormal bite can contribute to bruxism. Corrective dental treatments might be necessary.
- Avoiding Hard Foods: Chewing on hard foods or objects can exacerbate the effects of bruxism. Avoid nuts, popcorn kernels, and ice, and do not use your teeth as tools.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Frequent check-ups can help monitor the progression of tooth attrition and other complications associated with bruxism.
- Medications: In some cases, medications such as muscle relaxants might be prescribed temporarily.
Lifestyle Changes for Relief
- Reduce caffeine and alcohol, as they can increase the tendency to grind your teeth.
- Practice good sleep habits to improve the quality of your sleep and reduce grinding.
- Be conscious of not clenching your teeth during the day. Place the tip of your tongue between your teeth to train your jaw muscles to relax.
In conclusion, teeth grinding is a condition that should not be overlooked, given its potential to cause tooth attrition and other oral health issues. If you suspect you might be grinding your teeth, consult with your dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With the right care, grinding and its effects can be managed effectively. Contact Blashford Dentistry to learn more about how you can prevent teeth grinding, as well as restore your healthy smile.